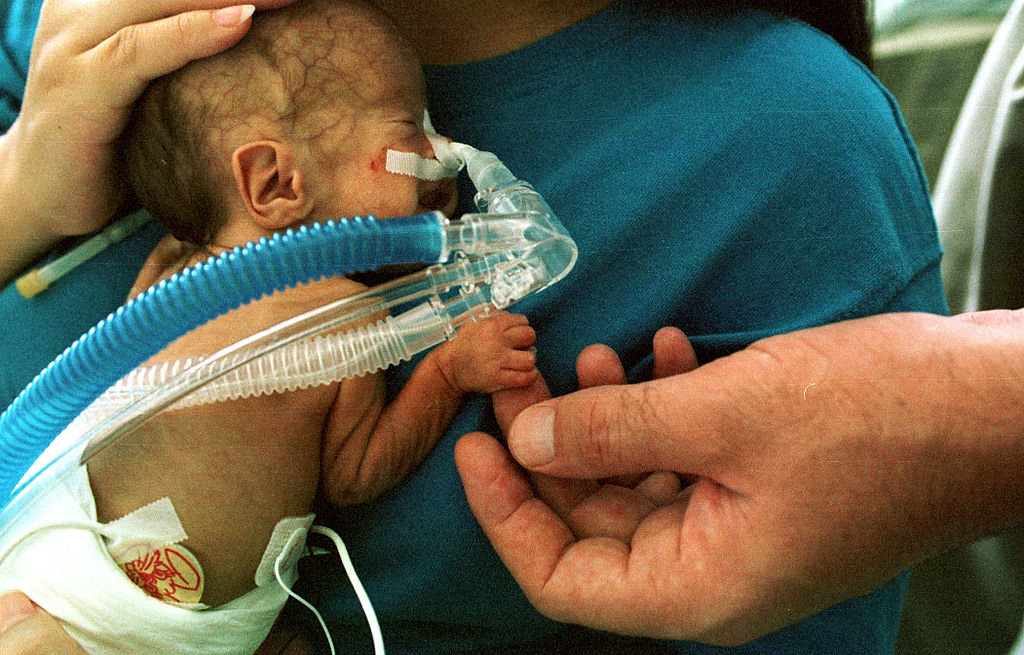
The word preterm is derived from the Latin word prae(before) and the Greek word terma(limit). In 1977, the World Health Organisation (WHO) defined preterm birth as birth before 37 completed weeks of gestation or fewer than 259 days from the first day of the last menstrual period.
As per statistics provided by WHO, an estimated 15 million babies are born too early every year. That is more than 1 in 10 babies. Approximately, 1 million children die each year due to the complications of preterm birth.
Globally, more than 10 % of all the babies born are preterm. Preterm birth is the most important cause of neonatal mortality and the second-leading cause of death before age of 5 (after pneumonia) worldwide.
Preterm birth is a matter of global concern. However, more than 60% of preterm births occur in Africa and South Asia. In the lower-income countries, on average, 12% of babies are born too early compared with 9% in higher-income countries. Within countries, poorer families are at higher risk.
On the basis of how earlier they are born, Preterm babies can be further divided into three subcategories:
- extremely preterm (less than 28 weeks)
- very preterm (28 to 32 weeks)
- moderate to late preterm (32 to 37 weeks).
Complications Due to Premature Birth of a Baby
- Prolonged Hospital stay
- Mortality risk is much higher than for a newborn at term.
- Difficult adaptation to life outside the womb.
- Hypoglycemia, respiratory distress, apnea, temperature instability, digestive disorders: jaundice or external feeding difficulties.
- Increased susceptibility to infections, especially respiratory tract infections, asthma, hypertension.
- Visual and hearing deficits : myopia, deafness, growth retardation in stature-weight
- Neurological problems, such as paralysis or cerebral atrophy, increased risk of autism (especially in the case of the late premature)
Risk factors that Cause Premature Birth of a Baby(Complex and Multifactorial)
- Approximately two-thirds of preterm births are spontaneous, and the causes are largely unknown
- Maternal factors (local and general) – Age : under 16 or over 45 years
- Height of mother below 145 cm
- Pre-pregnancy weight less than 45kg
- Low socioeconomic level
- Excessive physical effort
- Gynecological and obstetrics history – within less than a year after a previous birth
- History of premature births
- History of repeated miscarriages or abortions
- Smoking and alcohol
- Drugs
- Caffeine
- Occupational poisoning with lead, mercury
- Excessive sexual activity in the last trimester of pregnancy
- Multiple pregnancies
- Infections and chronic conditions such as diabetes and high blood pressure.
- There could also be a genetic influence
- Greater use of infertility treatments leading to increased rates of multiple pregnancies, and changes in obstetrics practices such as more cesarean births before terms
- Poor oral health and gum infections