“Let food be thy medicine and medicine be thy food”
Hippocrates
Human intestine or gut is not sterile. Microbes start colonizing human gastrointestinal tract soon after birth. Since birth, commensal gut bacteria is essential to the development of many intestinal functions, structures and immune system.
The human gut may contain microflora of over 35, 000 bacterial species ( An organ within an organ). The equilibrium that exists in the intestine is dynamic and is affected by age, diet composition and other environmental factors.
The gut microflora in an infant starts resembling the adult flora by the age of 3 years. Therefore, early factors can greatly affect the make-up and composition of the human gut microbiota, which may have consequences for intestinal development and the risk of diseases.
Factors Responsible for Shaping the Normal Gut Microflora
- The mode of delivery (vaginal or cesarean)
- Diet during infancy (breast milk or formula feeds), and adulthood (vegan based or meat based)
- Use of antibiotics or antibiotic like molecules that are derived from the environment or the gut flora.
Healthy gut flora is largely responsible for the overall health of the host. It plays a crucial role in digestion, nutrition and metabolism,(e.g., the regulation of cholesterol absorption, blood pressure (BP), and glucose metabolism), inflammation and cell proliferation, protection from pathogens and development of the immunity.
Changes and imbalances in gut microbes are associated with altered health state: inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), gastroenteritis, metabolic diseases such obesity and diabetes, allergic disease, colon cancer and neurodevelopmental illnesses. A healthy gut is very essential, even for the health of distant organs and bodily systems.
Prebiotics vs. Probiotics
While Prebiotics and Probiotics sound similar, they are not the same. Although both these supplements have aims of improving overall intestinal health both have different roles in the digestive system (or gut).
What is Prebiotics?
Prebiotics are nonviable food component that confers a health benefit on the host associated with modulation of the microbiota. (Food Agriculture Organization (FAO)/WHO 2007).
Selection criteria for Prebiotic?
- Resistance to digestion in the upper sections of the alimentary tract
- Fermentation by intestinal microbiota.
- The beneficial effect on the host’s health.
- Selective stimulation of growth of probiotics.
- Stability in various food/feed processing conditions
How does Prebiotics act?
- Prebiotic goes through the small intestine undigested and is fermented when it reaches the large intestine.
- This fermentation process feeds beneficial bacteria colonies (including probiotic bacteria) and helps to increase the number of desirable bacteria in the gut.
- Products of fermentation: Short chain fatty acids, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, and methane may have beneficial effects both to the gut environment and the host.
Various Sources of Prebiotics
- Some of the sources of prebiotics include breast milk, soybeans, inulin sources (like Jerusalem artichoke, chicory roots etc.), raw oats, unrefined wheat, unrefined barley, yacon.
- Non-digestible carbohydrates fructans – fructooligosaccharides (FOS) and inulin, galactooligosaccharides (GOS), polydextrose, resistant starch, soy oligosaccharides, xylooligosaccharides, isomaltooligosaccharides, and lactulose.
- In infant formula, most of the time galactooligosaccharides (GOS) and/or fructooligosaccharides (FOS) are used.
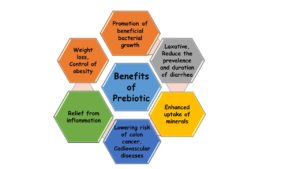
Benefits of Prebiotics
What are Probiotics?
The word “Probiotic” comes from Greek, means “for life” Probiotics are defined by them as “live microorganisms which when administered in adequate amounts confer a health benefit on the host”(Food Agriculture Organization (FAO)/WHO 2001).
Selection criteria for Probiotic
- The beneficial effect on the host
- Withstand into a foodstuff at high cell counts
- Remain viable throughout the shelf life of the product
- Withstand transit through the gut
- Adhere to intestinal epithelial cell lining and colonize the lumen of the track
- Produce antimicrobial substances towards the pathogens
Various Sources of Probiotics
These bacteria are naturally created by the process of fermentation in foods like cheese, yoghurt, sauerkraut, miso soup (prepared from fermented soy, rye, beans, barley or rice), kimchi (Korean side dish). Probiotics are also available in pill form and as an added ingredient in products like yoghurt and health drinks. Other sources are Dark Chocolate, Pickles, soy milk, olives, Idly, Dosa And Other South-Indian Cuisine, Dhokla.
Probiotics include a large number of species of microorganisms, Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, Lactococcus, Streptococcus, Enterococcus, Saccharomyces (yeast). Most commonly used: Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium.
- Lactobacillus – Most common probiotic found in yoghurt and other fermented foods. It is a good option for those who have diarrhoea and people who can’t digest milk sugar (lactose).
- Bifidobacterium –Naturally present in the large intestine, bifidobacteria fight harmful bacteria in the intestines, prevent constipation and give the immune system a boost. It is also found in some dairy products. May ease symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and related conditions. Furthermore, evidence indicates that bifidobacteria help reduces intestinal concentrations of certain carcinogenic enzymes.
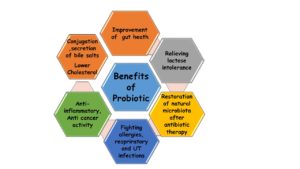
Benefits of Probiotics
Points to Remember before buying Probiotic
- All the probiotic products are not alike
- How probiotics work may depend on the strain, dose, and components used to produce a given probiotic product.
- They do not have similar nutritional and therapeutic attributes.
- To reap the benefits of Probiotic it is mandatory to choose Probiotic with the right strain, in the right amount, in the right formulation and right condition (viable) for the intended use.
- Probiotics should be safe and produced desirable benefits.
- Additionally, they should be least modified during production, manufacturing, distribution and storage prior to reaching to the consumer.
How much Prebiotics and Probiotics to add?
- The minimum effective dose of ≥108 CFU/day has been recommended for therapeutic effects during the FAO/WHO consultation meeting in 2001.
- The minimum dose of 109 CFU/day and consumption of 100 g or ml (a food containing at least 107 cells per gram or millilitre) was recommended for dairy products by the Japanese Fermented Milk and Lactic Acid Bacteria Beverages Association.
Synbiotics
“Synbiotics” come on the market. These are combinations of a prebiotic and most of the time several strains of probiotics which act synergistically.
- Increased Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium genus count and maintenance of a balance of the intestinal microbiota.
- Improved hepatic function in patients suffering from cirrhosis.
- Improved immunomodulatory abilities.
- Prevention of bacterial translocation and reduced incidence of nosocomial infections in patients’ post-surgical procedures.